Step-by-Step Guide to Calibrating Your Pressure Transmitter
Understanding Pressure Transmitter Calibration
Accurate pressure measurement is crucial in many industries, from oil and gas to food processing. A well-calibrated pressure transmitter ensures precise readings, enhancing safety and efficiency. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of calibrating your pressure transmitter, helping you maintain optimal performance and reliability in your operations.
Understanding Pressure Transmitter Calibration
Calibration is the process of comparing a measuring device against a standard of known accuracy. For pressure transmitters, this involves applying a known pressure and adjusting the transmitter's output to match. Regular calibration is essential to maintain accuracy and comply with industry standards.
Why Calibration Matters?
Proper calibration of your pressure transmitter is critical for several reasons:
- Ensures measurement accuracy
- Maintains compliance with industry regulations
- Extends the lifespan of your equipment
- Improves process efficiency and product quality
- Reduces the risk of equipment failure and downtime
Frequency of Calibration
The frequency of calibration depends on various factors, including:
- Manufacturer recommendations
- Industry standards and regulations
- Environmental conditions
- Criticality of the measurement
Generally, it's advisable to calibrate pressure transmitters annually, but some applications may require more frequent calibration.
Essential Tools for Pressure Transmitter Calibration
Before beginning the calibration process, gather the necessary tools and equipment. Having the right tools ensures a smooth and accurate calibration procedure.
Calibration Equipment
The following equipment is essential for calibrating your pressure transmitter:
- Pressure calibrator or dead weight tester
- Multimeter for measuring electrical output
- Power supply (if required by your pressure transmitter)
- Pressure source (e.g., hand pump or nitrogen cylinder)
- Adapters and fittings to connect the pressure transmitter to the calibration equipment
Safety Equipment
Safety should always be a priority when working with pressure equipment. Ensure you have:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses and gloves
- Proper ventilation in the work area
- Pressure relief valve for emergency depressurization
Step-by-Step Calibration Process
Follow these steps to calibrate your pressure transmitter accurately:
Preparation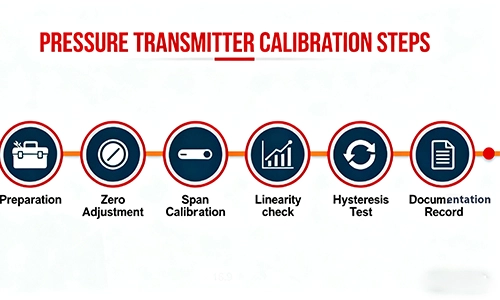
Before starting the calibration process:
- Review the manufacturer's manual for your specific pressure transmitter model
- Ensure all equipment is in good working condition
- Allow the pressure transmitter to stabilize at room temperature
- Disconnect the pressure transmitter from the process
Zero Adjustment
Begin with zero adjustment:
- Connect the pressure transmitter to the calibration equipment
- Apply zero pressure (venting to atmosphere for gauge pressure transmitters)
- Adjust the zero point if necessary, following the manufacturer's instructions
Span Calibration
Next, perform the span calibration:
- Apply the full-scale pressure to the pressure transmitter
- Adjust the span setting to match the applied pressure
- Verify the output signal corresponds to the full-scale pressure
Linearity Check
Check the linearity of the pressure transmitter:
- Apply pressures at 25%, 50%, and 75% of the full scale
- Record the output at each point
- Verify that the output is linear across the range
Hysteresis Test
Perform a hysteresis test:
- Increase pressure from zero to full scale, then decrease back to zero
- Record readings at each point during both ascent and descent
- Compare the readings to check for any significant differences
Documentation
Proper documentation is crucial:
- Record all calibration data, including date, time, and environmental conditions
- Note any adjustments made during the calibration process
- Generate a calibration certificate if required
Avoiding Common Calibration Errors
Be aware of these common pitfalls to ensure accurate calibration of your pressure transmitter:
Neglecting Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions can significantly impact calibration accuracy:
- Temperature fluctuations can affect both the pressure transmitter and calibration equipment
- Vibrations may interfere with readings
- Electromagnetic interference can disrupt electronic signals
Always calibrate in a stable environment and account for any environmental factors that could affect the results.
Improper Zeroing
Failure to properly zero the pressure transmitter can lead to systemic errors across the entire range. Ensure that:
- The pressure transmitter is fully vented before zeroing
- There are no residual pressures in the system
- The zero point is stable before proceeding with span calibration
Overlooking Hysteresis
Hysteresis in pressure transmitters can lead to inaccurate readings. To avoid this:
- Always perform both ascending and descending pressure tests
- Compare the results to identify any significant hysteresis
- If hysteresis is excessive, consult the manufacturer or consider replacing the pressure transmitter
Understanding Accuracy in Pressure Transmitters
Accuracy is a critical specification for pressure transmitters. It's essential to understand what accuracy means and how it affects your measurements.
Defining Accuracy
Accuracy in pressure transmitters typically includes several factors:
- Linearity: The deviation from a straight-line relationship between input and output
- Hysteresis: The difference in output for the same input when approaching from different directions
- Repeatability: The ability to produce the same output for repeated identical inputs
Manufacturers often express accuracy as a percentage of full scale or span.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
 Several factors can impact the accuracy of your pressure transmitter:
Several factors can impact the accuracy of your pressure transmitter:
- Temperature effects on zero and span
- Static pressure effects (for differential pressure transmitters)
- Long-term stability and drift
- Mounting position effects
Understanding these factors helps in selecting the right pressure transmitter for your application and maintaining its accuracy over time.
Conclusion
Calibrating your pressure transmitter is a crucial maintenance task that ensures accurate measurements and reliable operation. By following this step-by-step guide and avoiding common errors, you can maintain the performance of your pressure transmitters and optimize your processes. Remember that while regular calibration is essential, it's equally important to choose high-quality pressure transmitters suited to your specific application needs.
Experience the Precision of GAMICOS Pressure Transmitters
GAMICOS, a leading manufacturer of pressure and level measurement solutions, offers a wide range of high-precision pressure transmitters, including the advanced GPT241 series. Our products feature single-crystal silicon sensors, excellent temperature stability, and strong resistance to overload and corrosion. With extensive experience serving clients in 98 countries, GAMICOS provides customized solutions, professional technical support, and comprehensive after-sales service. For unparalleled accuracy and reliability in your pressure measurement applications, choose GAMICOS. Contact us at info@gamicos.com to explore how our expertise can elevate your measurement capabilities.
References
1. Smith, J. (2021). "Principles of Pressure Transmitter Calibration." Journal of Instrumentation Technology, 15(3), 78-92.
2. Johnson, R. & Williams, T. (2020). "Best Practices in Industrial Pressure Measurement." 3rd ed. New York: Industrial Press.
3. International Society of Automation. (2019). "ISA-75.01.01-2019: Flow Equations for Sizing Control Valves."
4. Brown, A. (2022). "Advances in Pressure Transmitter Technology." Sensors and Transducers Magazine, 28(4), 112-125.
5. National Institute of Standards and Technology. (2021). "Guidelines for Pressure Calibration in Industry." NIST Special Publication 250-39r2.

Peter
Peter, Senior Sensor Technology Consultant, has 15-year industrial sensor R&D experience. He specializes in the end-to-end development of high-accuracy pressure and level sensors and he firmly believe, precision isn’t just a spec—it’s a promise.
We're here to help — submit your request anytime!
Let us know how we can help solve your pressure level measurement challenge.
Recommended Blog

_1757930850792.jpg)








